In the high-stakes world of space exploration, redundancy isn’t just a luxury—it’s a lifesaver. As we look to the future of space travel with vehicles like Boeing’s Starliner, it’s crucial to understand how spacecraft can overcome potential failures, especially in critical systems like thrusters. Let’s take a fascinating journey back to the Apollo era to see how these lessons are still relevant today for Surviving a Thruster Failure in Space.
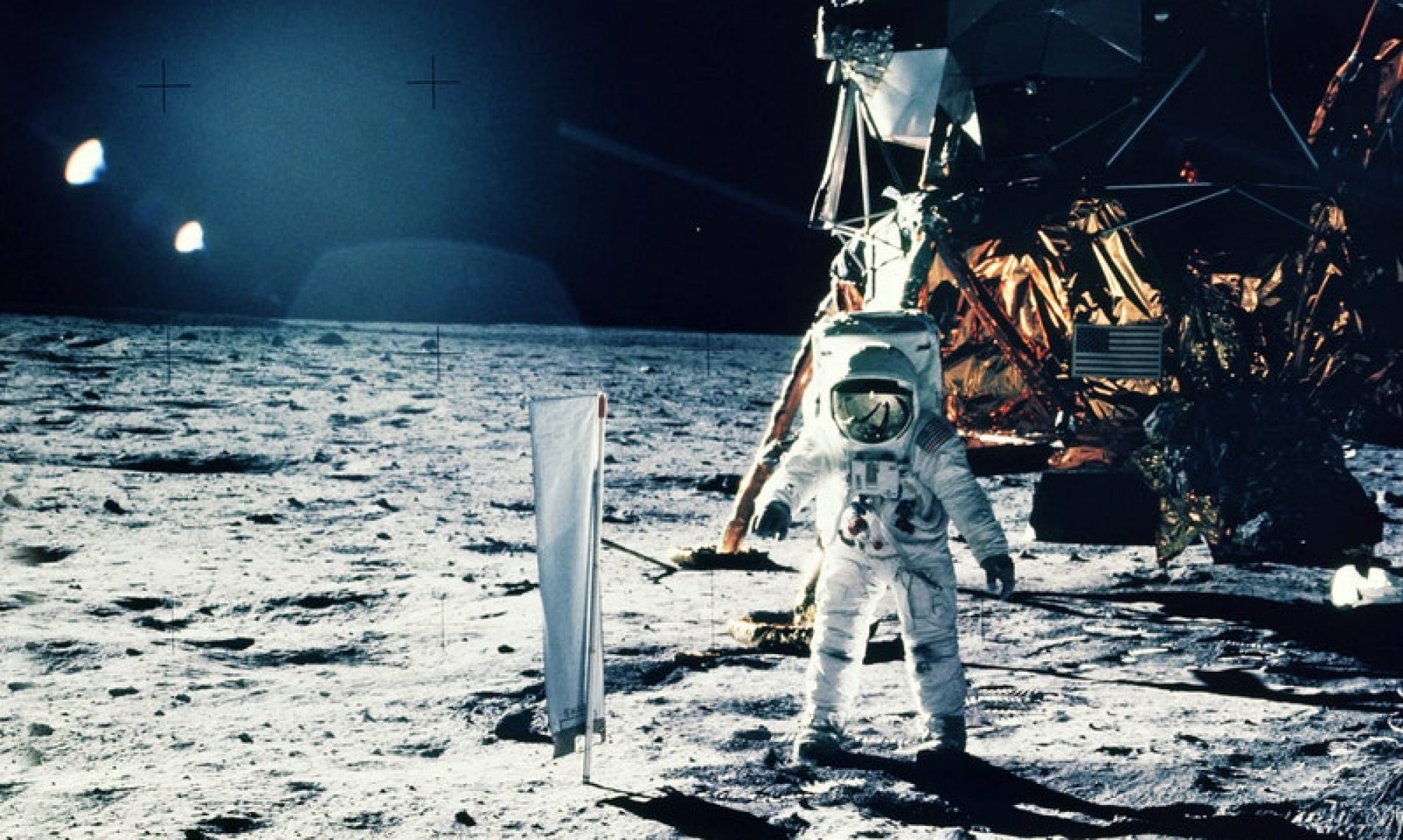
Imagine you’re returning from the Moon in a lunar lander. Suddenly, one of your thrusters malfunctions. How do you make it back safely? This isn’t just a hypothetical scenario—it’s a real concern that engineers have grappled with since the dawn of space exploration.
Surviving a Thruster Failure in Space in the Past
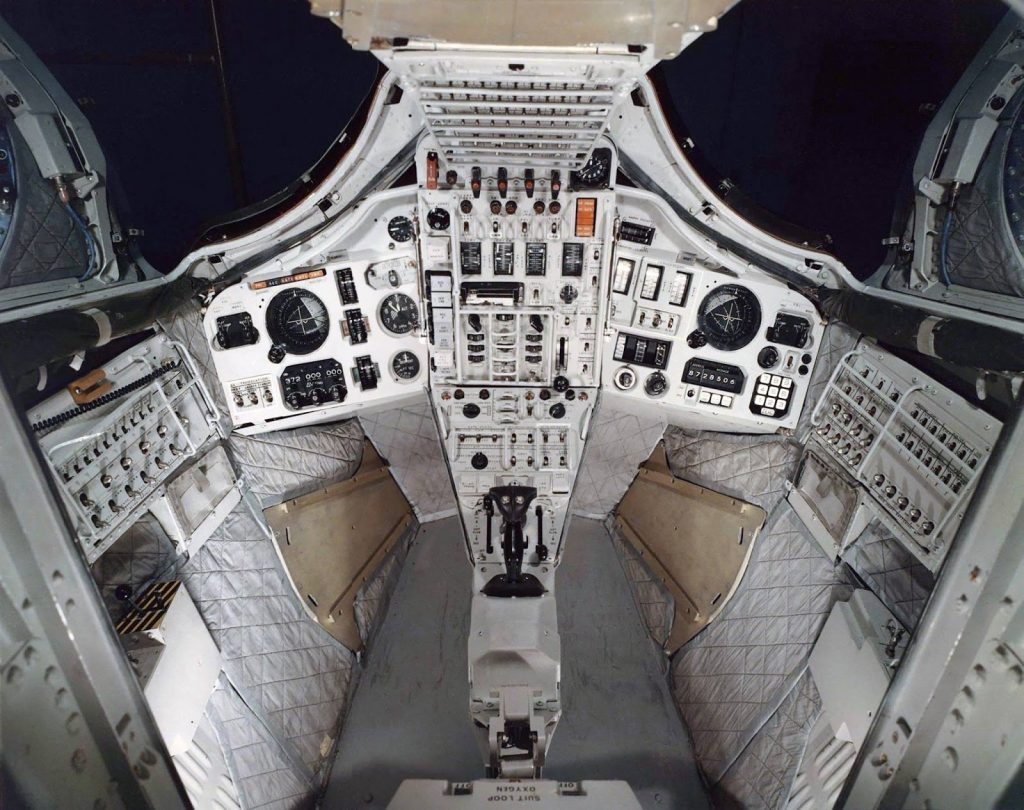
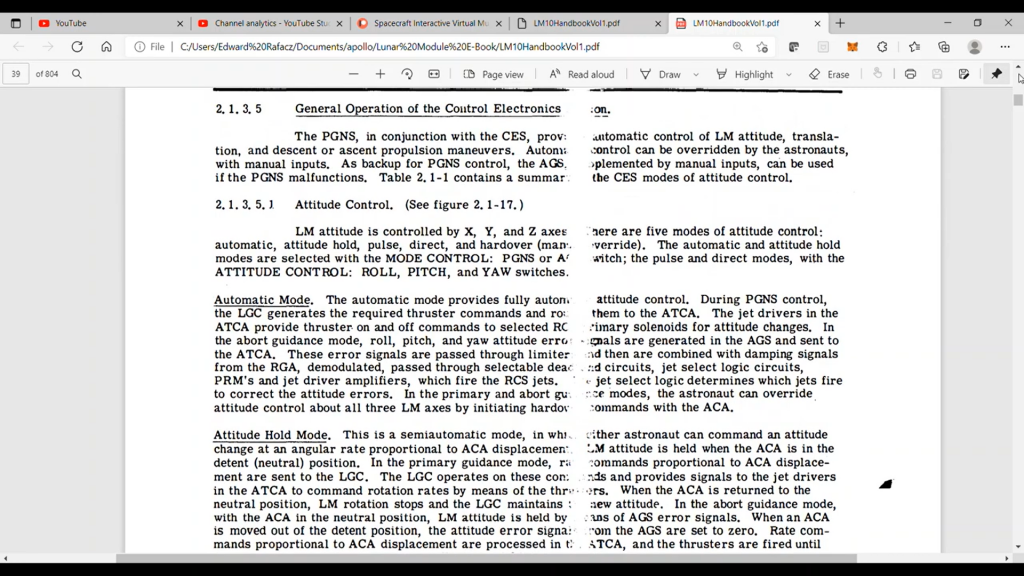
The Apollo lunar module, like modern spacecraft, was designed with multiple layers of redundancy. One key system was the Reaction Control System (RCS), responsible for attitude control and minor course corrections. Here’s how it worked:
- Dual Pressurization Systems: The RCS had two separate helium pressurization systems (A and B). If one failed, the other could take over.
- Redundant Valves: Each system had multiple valves, ensuring that if one stuck, others could compensate.
- Quad Thrusters: Thrusters were arranged in quads, allowing for backup if one thruster failed.
- Isolation Capability: Engineers could isolate problematic thruster quads using “thrust pair command quad switches,” preventing fuel loss and maintaining control.
This level of redundancy meant that even if multiple components failed, astronauts still had options for controlling their spacecraft and returning home safely.
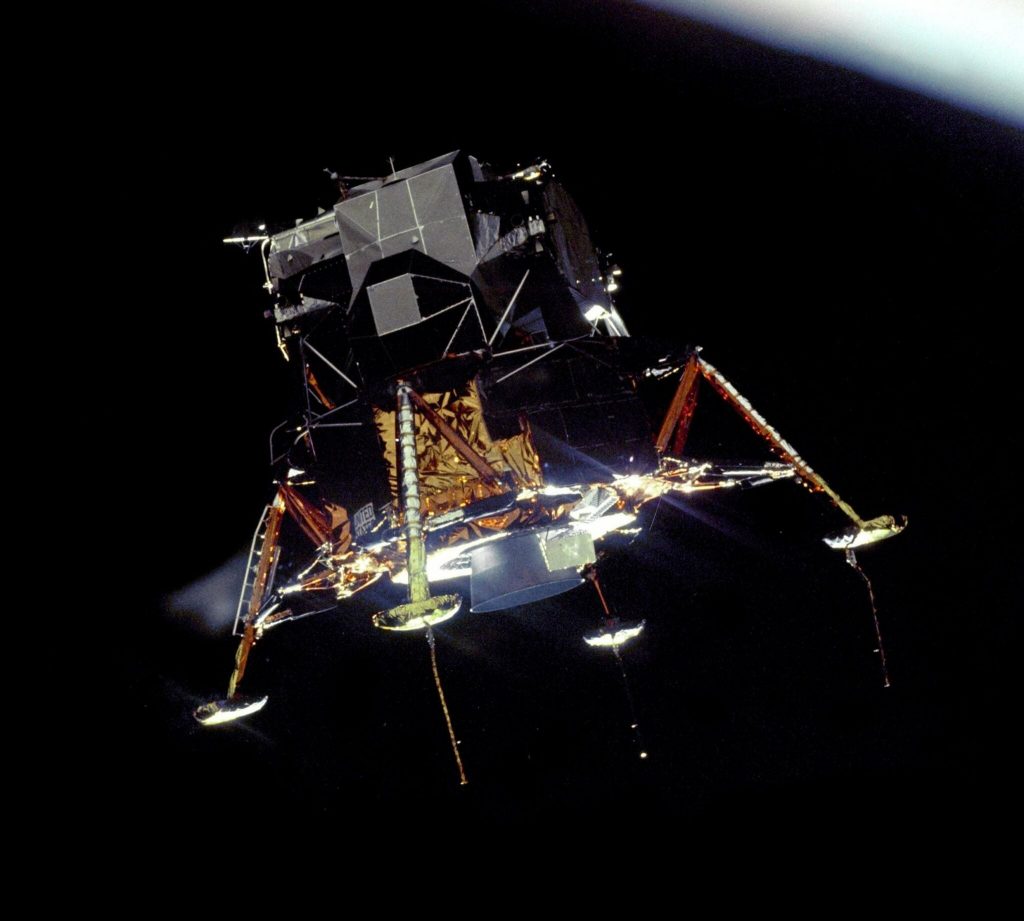

Surviving a Thruster Failure in Space Today
Fast forward to today’s Starliner: While the specifics differ, the principles remain the same. Modern spacecraft incorporate multiple layers of redundancy in critical systems. For instance, Starliner features:
- Redundant thrusters for orbital maneuvering and attitude control
- Backup flight computers
- Multiple power systems
These design choices reflect the lessons learned from Apollo and other space programs, ensuring that even if something goes wrong, there’s always a backup plan.

Understanding these systems isn’t just for astronauts and engineers. As space tourism becomes a reality, future passengers might find comfort in knowing how their spacecraft can handle potential failures. It’s a testament to human ingenuity and our unwavering commitment to making space exploration as safe as possible.
The next time you hear about a spacecraft launch or see the Starliner dock with the International Space Station, remember the intricate systems working behind the scenes. They’re the unsung heroes of space travel, quietly ensuring that even in the face of adversity, we can still find our way home from the stars.
Support Us: Elevate Your Experience for $4 a Month
Our new format promises a richer experience. For just four dollars a month, you’re not only supporting a passion project but becoming an integral part of it. Join us in this cosmic journey; your support makes our interactive virtual exhibits even more stellar. Spacecraft Interactive Virtual Museum | creating Interactive Virtual Museum Exhibits | Patreon
Stay tuned for more cosmic revelations. Spacecraft Guide continues to unravel the wonders of space, one switch at a time. Your support and curiosity drive us to bring the wonders of space to your screens at Blog – Spacecraft Guide. Until then, keep your eyes on the stars and your curiosity alive!