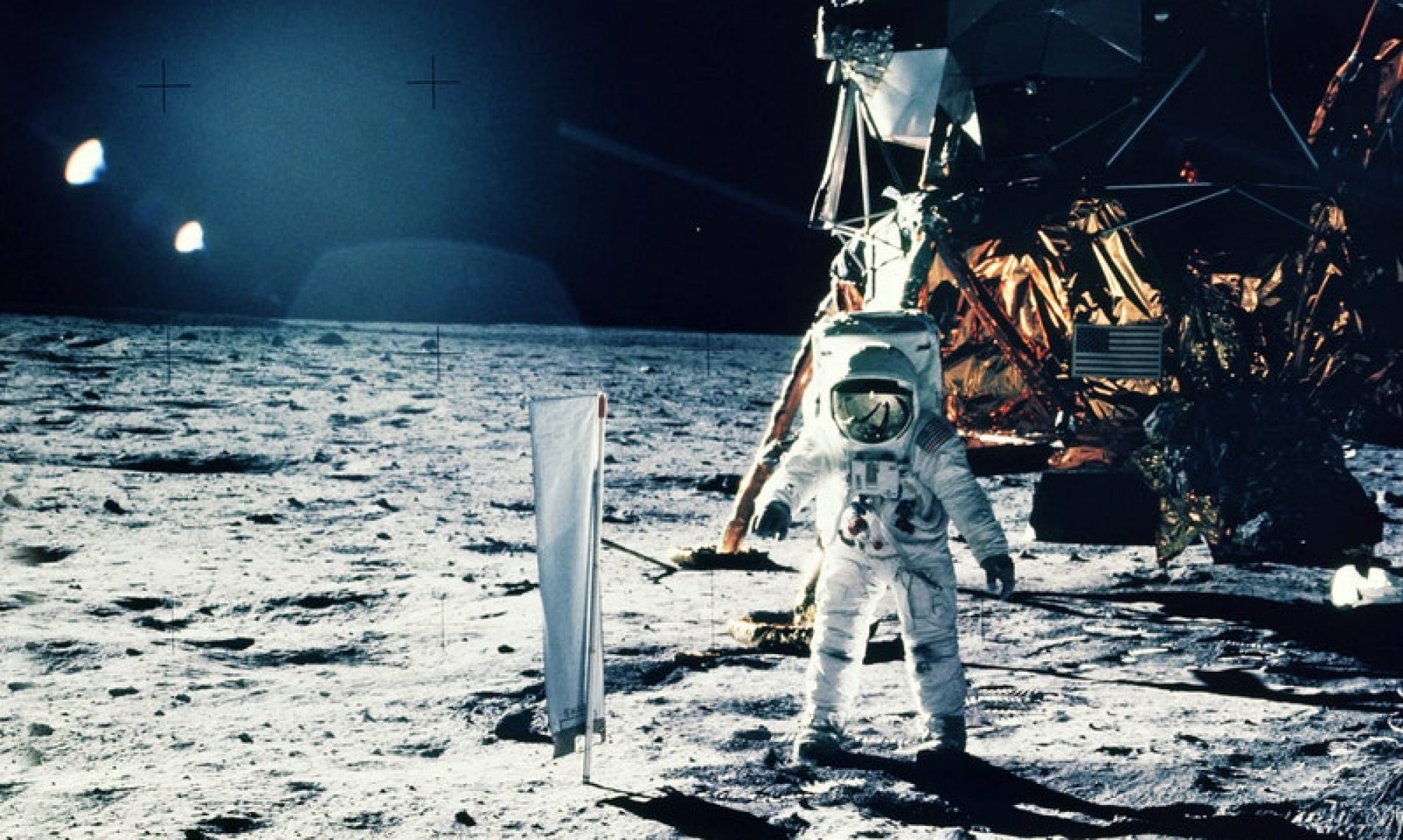
Unveiling the Electric Cosmic Control Panel: Navigating the Apollo LM Battery Feed Switches
Welcome back to Spacecraft Guide, your go-to channel for unraveling the mysteries of historic spacecraft! In this episode of the Spacecraft Guide, we’re diving deeper into the electrical panel, putting the spotlight on switches that made lunar missions possible. We’ll demystify the Battery 5 Normal LMP Feed Switch, the Battery 5 Normal Commander Feed Switch, the Battery 6 Normal Commander Feed Switch, and the Battery 6 Normal LMP Feed Switch. These may sound technical, but we’re here to break it down for you.
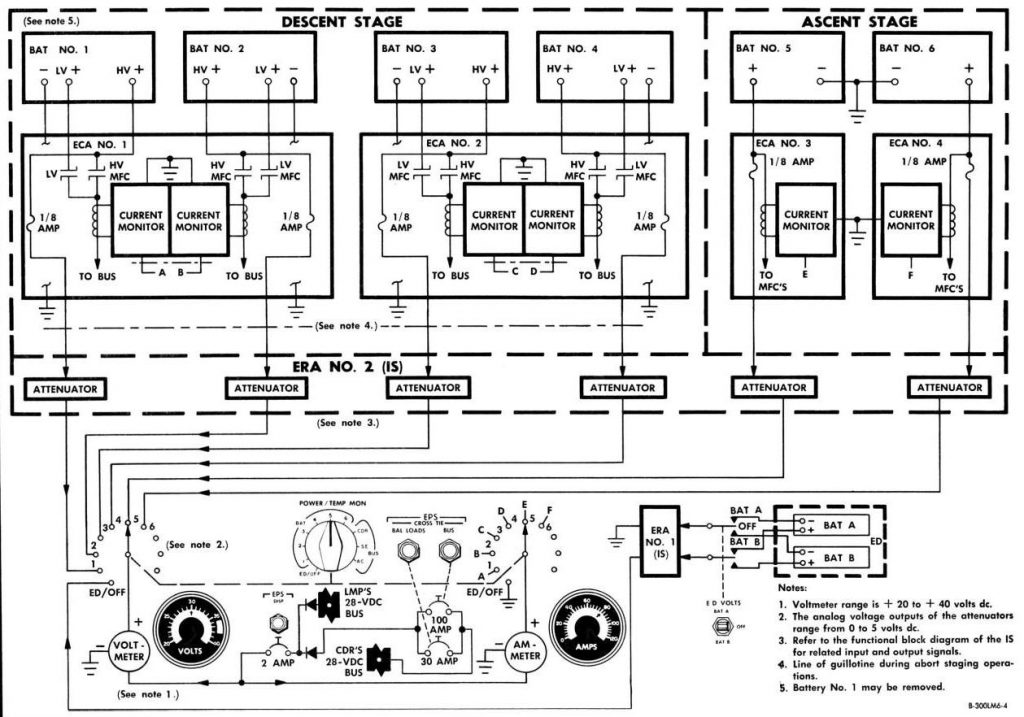
The Cosmic Switchboard:
When you click on one of these switches, you’re transported to its world. Whether it’s Battery 5 or 6, the Lunar Module Pilot or Commander Feed Switch, each has a crucial role. These LM Battery Feed Switches control the connections of a sense battery to the bus, ensuring a steady flow of power.
Operation and Safety:
These switches are no ordinary toggles; they come with built-in safety features. They can disconnect the battery from the DC bus in case of overcurrent, a safety measure that’s crucial in space. In the event of overcurrent, these switches disconnect the ascent battery and reset the connectors for overcurrent protection. A fail-safe, ensuring astronauts’ safety even amidst the most challenging conditions.
Behind the Click of the LM Battery Feed:
What’s fascinating is how a single click on one of these switches holds the power to reset a whole network, protecting vital systems. It’s a testament to the meticulous engineering that went into the Apollo program.
What’s Next:
But that’s not all! The journey doesn’t end here. If you want to explore the interactive virtual reality exhibit on the Command Module, Lunar Module, and even the Moon’s surface, head over to our the Spacecraft Virtual Reality Spacecraft Museum Exhibit Patreon page. The link is waiting to transport you to the cosmos.
Thanks for joining us in this cosmic exploration of switches that were the lifeline of lunar missions. We hope this journey behind the panels has been enlightening. Remember, the Apollo program was a marvel of human achievement and ingenuity, and these switches played a hidden but vital role in its success. If you enjoyed this episode, don’t forget to like, subscribe, and share your thoughts. Our Spacecraft Virtual Reality Spacecraft Museum Exhibit Patreon page is there for the space enthusiasts who want to delve even deeper into these fascinating spacecraft. Until next time, keep gazing at the stars and reaching for the cosmos! 🌌🚀
Thank you for watching this video to the end. Every click, every share, every subscription propels us further into the unknown. Your support fuels our passion for space exploration. From the Spacecraft Virtual Reality Spacecraft Museum Exhibit team, thank you! #SpaceExploration #Apollo11 #VirtualMuseum
https://www.youtube.com/embed/1t4LIFboAIk?feature=oembedHow to Turn Your Phone into a VR Viewer
https://www.youtube.com/embed/1t4LIFboAIk?feature=oembedTurn This post into an immersive vr experience below!
Get the best DEAL on Google Cardboard Here
5 Pack Deal – Best bulk Deal on Google Cardboard I have found.
Note: Prices and availability of VR headsets may vary. Please check local retailers or online stores for the most up-to-date information.


